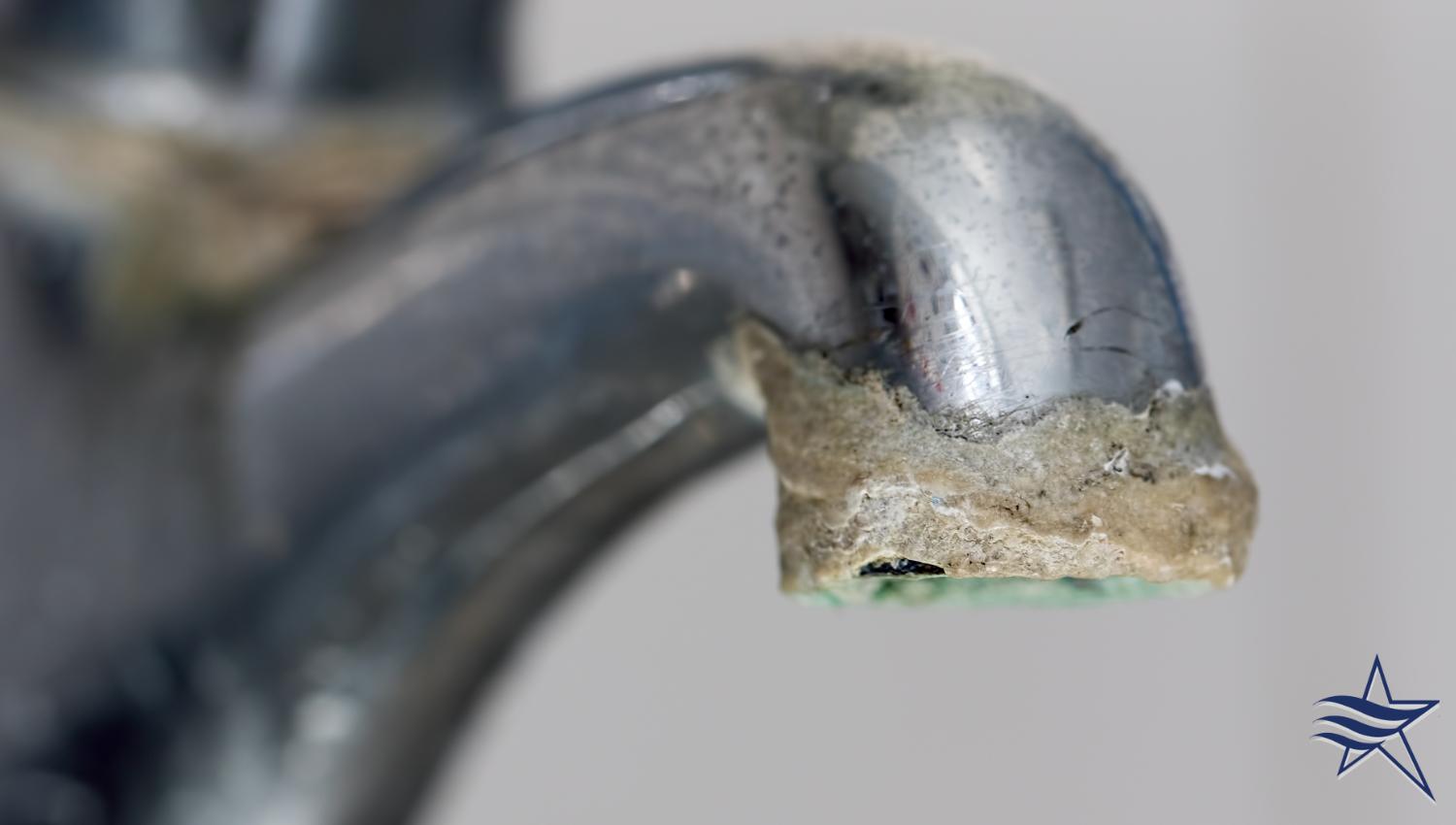
Hard water is a common concern that affects homes across Carrollton, TX. But what exactly is hard water? Simply put, hard water contains high levels of minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium. While these minerals do not harm your health, they can wreak havoc on your plumbing system, appliances, and daily routines.
With Lex Air plumbing solutions, you can say goodbye to limescale buildup, spotted glassware, and the hassles of hard water!
What is Hard Water?
Hard water contains high concentrations of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium ions. This elevated mineral content occurs when water filters through geological formations rich in calcium and magnesium compounds, such as limestone and dolomite. These minerals are naturally present in the earth’s crust and dissolve into the water as it passes through these formations.
The hardness level of water is categorized into two main types:
- Temporary Hardness: This type of hardness is primarily due to the dissolved bicarbonate ions of calcium and magnesium. Boiling water can remove temporary hardness, which causes the bicarbonate ions to convert into carbonate ions and precipitate as solid calcium carbonate, commonly known as scale or limescale.
- Permanent Hardness: Permanent hardness is caused by calcium and magnesium ions in the form of sulfates or chlorides. Unlike temporary hardness, it cannot be removed by boiling and requires alternative treatment methods such as ion exchange, water softeners, or chemical additives.

How to Measure Water Hardness
Water hardness is typically measured in terms of calcium and magnesium ions concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or parts per million (ppm). These dissolved minerals are responsible for the characteristic traits of hard water, such as reduced soap lathering, scale buildup in pipes and appliances, and potential taste or texture differences in the water. The higher the calcium and magnesium concentrations, the harder the water becomes.
Water hardness is often classified into degrees of hardness, with the following general scale:
- Soft Water: 0-60 mg/L or ppm
- Moderately Hard Water: 61-120 mg/L or ppm
- Hard Water: 121-180 mg/L or ppm
- Very Hard Water: >180 mg/L or ppm
Hard Water vs. Soft Water
Water quality can significantly impact our daily lives, from household chores to the taste of our beverages. Hard water and soft water exhibit distinct characteristics that influence their use in homes. Below, we’ll explain the differences between these two water forms to better understand their effects on cleaning, appliances, taste, and overall convenience.
Hard Water
- High levels of calcium and magnesium minerals.
- Forms soap scum when mixed with soap or detergent, reducing cleaning efficiency.
- Leads to scale buildup in pipes and appliances, potentially reducing their lifespan.
- May have a distinct taste or texture due to mineral content.
- Often requires more maintenance and cleaning in households.
Soft Water
- Low levels of calcium and magnesium minerals.
- Lathers easily with soap and detergent, enhancing cleaning effectiveness.
- Minimizes scale buildup, extending the life of plumbing and appliances.
- Tends to have a smoother taste and texture, preferred by some for drinking and cooking.
- Generally demands less maintenance and cleaning in households.
Hard water has a high mineral content that can create challenges in cleaning, maintenance, and taste. In contrast, soft water, with its lower mineral content, offers improved cleaning efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements. The choice between them often depends on personal preferences and the specific needs of a household.

What Makes Water Hard?
Water becomes hard primarily due to dissolved minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium ions. These minerals enter the water as it flows through underground geological formations, such as limestone and dolomite, which are rich in calcium and magnesium compounds. When rainwater or surface water filters through these rock formations, it dissolves these minerals, making the water hard.
Is Hard Water Safe To Drink?
Yes, hard water is safe to drink. It may have a slightly different taste or texture due to its mineral content, but these minerals are not harmful to human health. Calcium and magnesium are essential minerals that can contribute to your daily dietary intake. Some people even prefer the taste of hard water.
The hardness of drinking water doesn’t pose a health risk. It’s the minerals in hard water that can affect the taste and texture but not the safety of the drinking water itself. If you have concerns about the taste or want to reduce the mineral content for aesthetic reasons, you can use a water softener or drink bottled water. Still, from a safety perspective, hard water is perfectly fine for use as drinking water.
Impacts of Hard Water
The impact of hard water extends beyond its mineral-rich composition. As a common issue in many households, understanding its effects is crucial for homeowners seeking solutions to maintain plumbing, appliances, and overall daily comfort. In this section, we’ll explain how it can influence the efficiency of your plumbing system, the longevity of your appliances, and even your everyday quality of life. Our Carrollton plumbing experts will also discuss the long-term repercussions of untreated hard water and whether it poses any health risks.
Plumbing
One of the most noticeable impacts of hard water is the accumulation of scale or limescale deposits in plumbing fixtures and pipes. These mineral deposits can reduce water flow, clog pipes, and decrease water pressure. The constant exposure to hard water also can lead to corrosion and damage to pipes and plumbing components, ultimately shortening their lifespan and requiring frequent repairs.
Appliances
Hard water can coat the heating elements inside water heaters with scale, reducing their efficiency and increasing energy consumption. Appliances like dishwashers and washing machines may experience reduced effectiveness due to hard water. Soap and detergent usually will not work as effectively, potentially leading to subpar cleaning results.
Daily Living
Hard water can make laundry less effective, leading to dull, faded clothing and stiff, scratchy fabrics. More detergent may be required to achieve satisfactory cleaning results. Hard water can also leave mineral residues on the skin and hair, making it difficult to lather soap and shampoo, causing dry, itchy skin and dull hair.
Long-Term Consequences
The constant exposure to hard water can result in prematurely replacing plumbing fixtures and appliances. Prolonged hard water exposure can also lead to frequent plumbing repairs, like pipe descaling and maintenance, which can add up over time. Hard water also reduces the energy efficiency of appliances, resulting in higher energy bills.
Health Risks
Hard water itself does not pose direct health risks. The minerals in hard water, such as calcium and magnesium, are not harmful when ingested in normal quantities and can even contribute to your daily dietary intake of essential minerals.
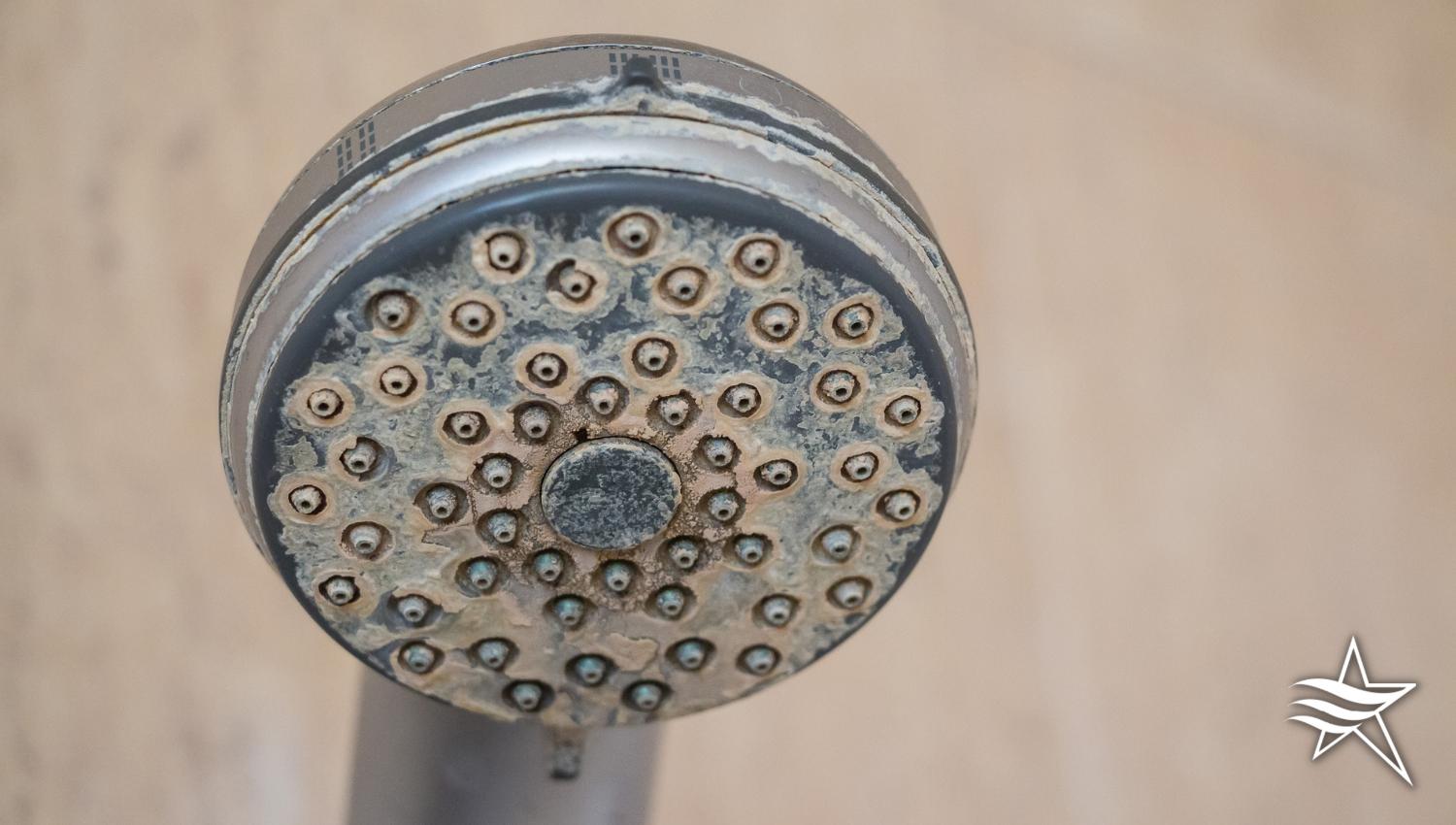

How To Tell If You Have Hard Water
Determining whether you have hard water in your home is important for addressing potential issues and making informed decisions about water treatment. Here’s how to tell if you have hard water:
- Inspect Faucets and Showerheads: Check for white or chalky deposits on faucets and showerheads. These mineral deposits, known as limescale, are a common indicator of hard water.
- Reduced Soap Lather
- Handwashing: When washing your hands, pay attention to how soap lathers. Hard water can make it more challenging to create a rich lather, resulting in a soapy residue that’s difficult to rinse off.
- Dishwashing: If your dishes, glassware, or silverware have a cloudy appearance or spots, even after using dishwasher detergent, it’s a sign of reduced soap effectiveness due to hard water.
- Spots on Glassware: After washing glassware, inspect for spots, streaks, or a cloudy appearance. These marks are often caused by mineral deposits left behind by hard water.
- Dry Skin and Hair: If you or your family experience dry, itchy skin or dull, lifeless hair, hard water may be the culprit. The minerals in hard water can leave residues on your skin and hair, making them less hydrated and vibrant.
- Scale in Appliances: Examine the interiors of appliances like coffee makers, kettles, and water heaters. Scale or mineral buildup on heating elements or surfaces is a clear sign of hard water.
- Soap Consumption: Monitor the amount of soap, shampoo, and detergent you use. If you’re using large amounts to properly lather and clean, it may indicate hard water.
- Water Stains: Look for water stains or marks on shower doors, fixtures, and bathroom tiles. These stains are difficult to remove and are often caused by the mineral deposits left behind when hard water dries.
In addition to looking out for the signs listed above, you can conduct some simple tests to determine your water hardness. Water hardness test kits are readily available online or at hardware stores. These kits typically include test strips that change color based on the water’s hardness.
How To Fix Hard Water
Dealing with the challenges posed by hard water is a common concern for homeowners across Carrollton. From scale buildup in plumbing systems to reduced soap lathering and the frustration of constantly battling soap scum, the impacts of hard water can be significant. Fortunately, effective solutions are available to address this issue and enjoy the benefits of softer, more manageable water.
Water Softeners
Water softeners remove the calcium and magnesium ions responsible for water hardness through ion exchange. Inside a water softener, resin beads attract and exchange these mineral ions for sodium or potassium ions, effectively softening the water.
Installing a water softener has many benefits, including reduced scale buildup in plumbing and appliances, improved soap and detergent efficiency, and softer, smoother skin and hair after bathing.
Descalers
Descalers are valuable tools for addressing the scale buildup caused by hard water. Unlike traditional water softeners that remove minerals, descalers work to prevent scale formation in the first place. These devices use electromagnetic or electronic technology to alter the structure of the calcium and magnesium ions, preventing them from adhering to surfaces and forming scales. Descalers offer a low-maintenance and environmentally friendly alternative to water softeners since they don’t require salt or chemicals.
Magnetic and Electronic Water Conditioners
Magnetic and electronic water conditioners are innovative technologies designed to address hard water issues without chemicals or salt. These devices work by adjusting the behavior of calcium and magnesium ions in the water to prevent them from forming scale buildup in plumbing and appliances.
Magnetic water conditioners use powerful magnets to create a magnetic field around the water pipes. This field affects the charge of mineral ions, making them less likely to adhere to surfaces. A magnetic water treatment device is relatively simple to install and requires no electricity. They are also eco-friendly and low-maintenance, providing a cost-effective solution for scale prevention.
Electronic water conditioners utilize electrical pulses or radio frequency waves to disrupt the crystal formation of mineral ions in hard water. By doing so, they inhibit scale buildup in pipes and appliances. These systems often come with adjustable settings to accommodate different water hardness levels and can be installed without cutting into the plumbing.
Preventive Measures and Regular Maintenance
To prevent scale buildup, consider installing water softeners or descaling devices that reduce mineral deposits in plumbing and appliances. Cleaning with vinegar or citric acid solutions to remove scale from faucets and showerheads can help keep fixtures in optimal condition.
It’s important to perform routine inspections of appliances like dishwashers and water heaters to assess hard water buildup and take the necessary actions to remove or reduce it. Cleaning and inspecting your appliances can also extend their lifespan. Homeowners should also consider installing water-saving and energy-efficient appliances that can reduce the overall impact of hard water and minimize maintenance requirements.

Alternative Methods for Managing Hard Water
For those seeking natural and DIY solutions to mitigate hard water’s effects, several options are available. One approach is to install water-saving showerheads and faucets, which can reduce the volume of water needed for effective cleaning and bathing.
Vinegar or lemon juice can be used as a natural cleaning agent to dissolve mineral deposits on fixtures and glassware. Another DIY solution is to boil water and allow it to cool before use, which can help reduce hard water’s impact.
When choosing soap, detergents, and shampoos, using products specifically formulated for hard water can enhance their effectiveness. Look for brands with added chelating agents that bind to mineral ions, preventing them from interfering with lathering and cleaning. These alternative methods and product choices can help homeowners manage hard water-related challenges more effectively.
Dealing With Hard Water in Your Carrollton Home? Lex Air Can Help
At Lex Air, we understand the significance of water quality in your daily life. That’s why our Carrollton plumbing experts specialize in identifying and resolving hard water issues by installing cutting-edge water filtration systems and water softeners.
If you’re tired of living with hard water, schedule a water filtration system consultation with one of our Lex Air plumbing experts by calling (972) 217-8955 or contacting us online today!












